ROLD GLOBAL EMISSION SYSTEM
ROLD SYNTHETIC DIGITAL CURRENCY (RSDC)
What is ROLD?
A non-sovereign, global emission system, subordinated to heterogeneous sovereign emissions, including their institutional and regulatory frameworks, interfacing with both fiat and crypto currency markets.
As a third-party system working with multiple sovereigns, ROLD breaks inter-sovereign stasis in the formulation of the next generation of global reserve currency and monetary exchange mechanisms.
Why is ROLD needed?
ROLD allows sovereigns to export their regulatory principles to all crypto and fiat transacting counterparties.
By accessing “regulated” crypto markets, ROLD opens up significant existing and potential new demand for sovereign emission.
ROLD enables crisis management by facilitating monetisation of high-risk assets to meet real demand for them.
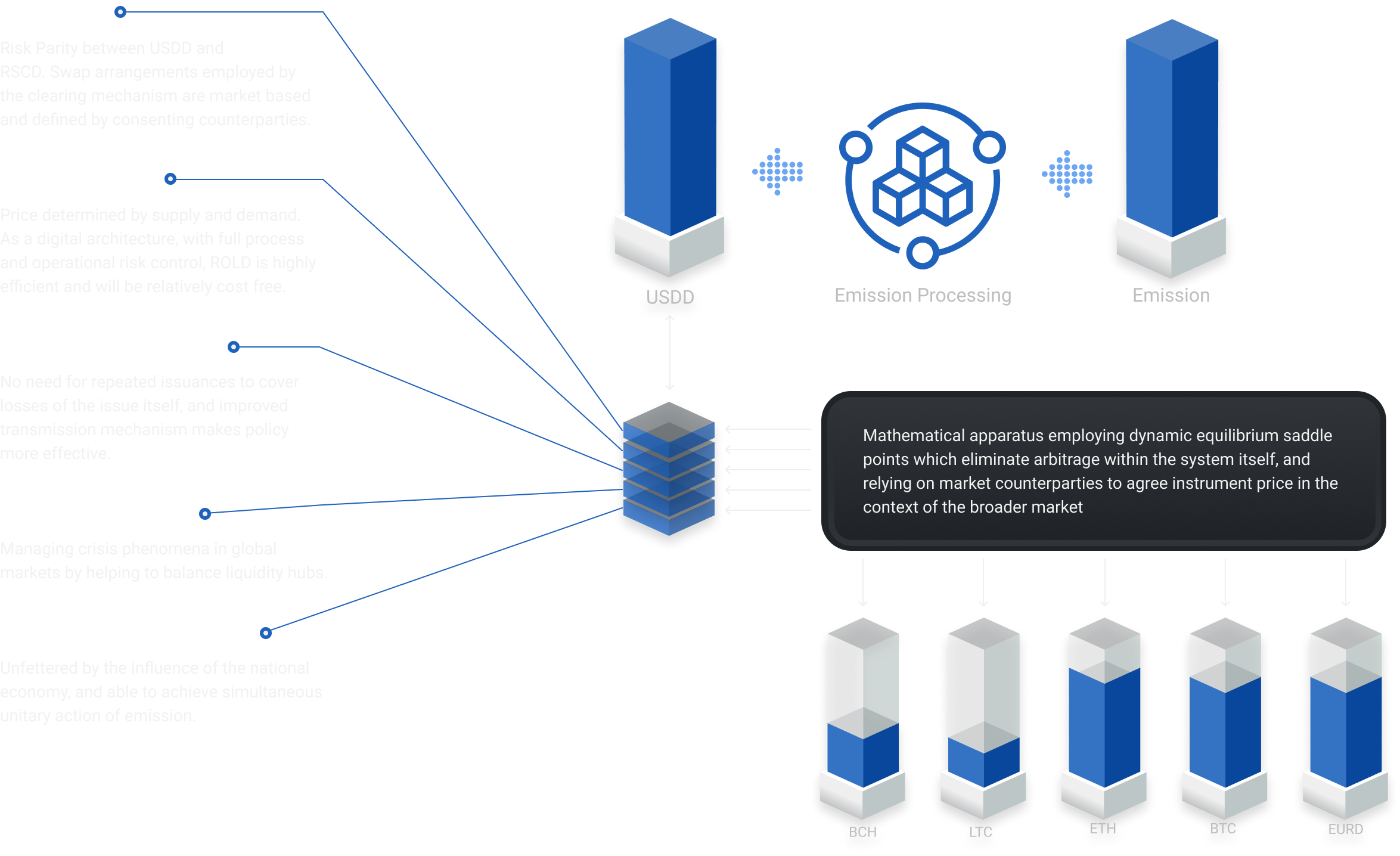
ROLD represents a new generation of risk, specifically, «sovereign synthetic risk», while eliminating substantial costs, risk and interactive negative feedback processes to all participating parties.
ROLD is available to address imbalances in the supply and demand of sovereign currencies, and thereby address the Triffin Dilemma, asset bubble accumulation, and other related side effects of the current system, including improved developing market contributions to global productivity and growth.
ROLD is available to expand and protect the role of the US Dollar as the main global reserve currency, in both the fiat and in the emergent digital/crypto ecosystem.
Costly Emission Process
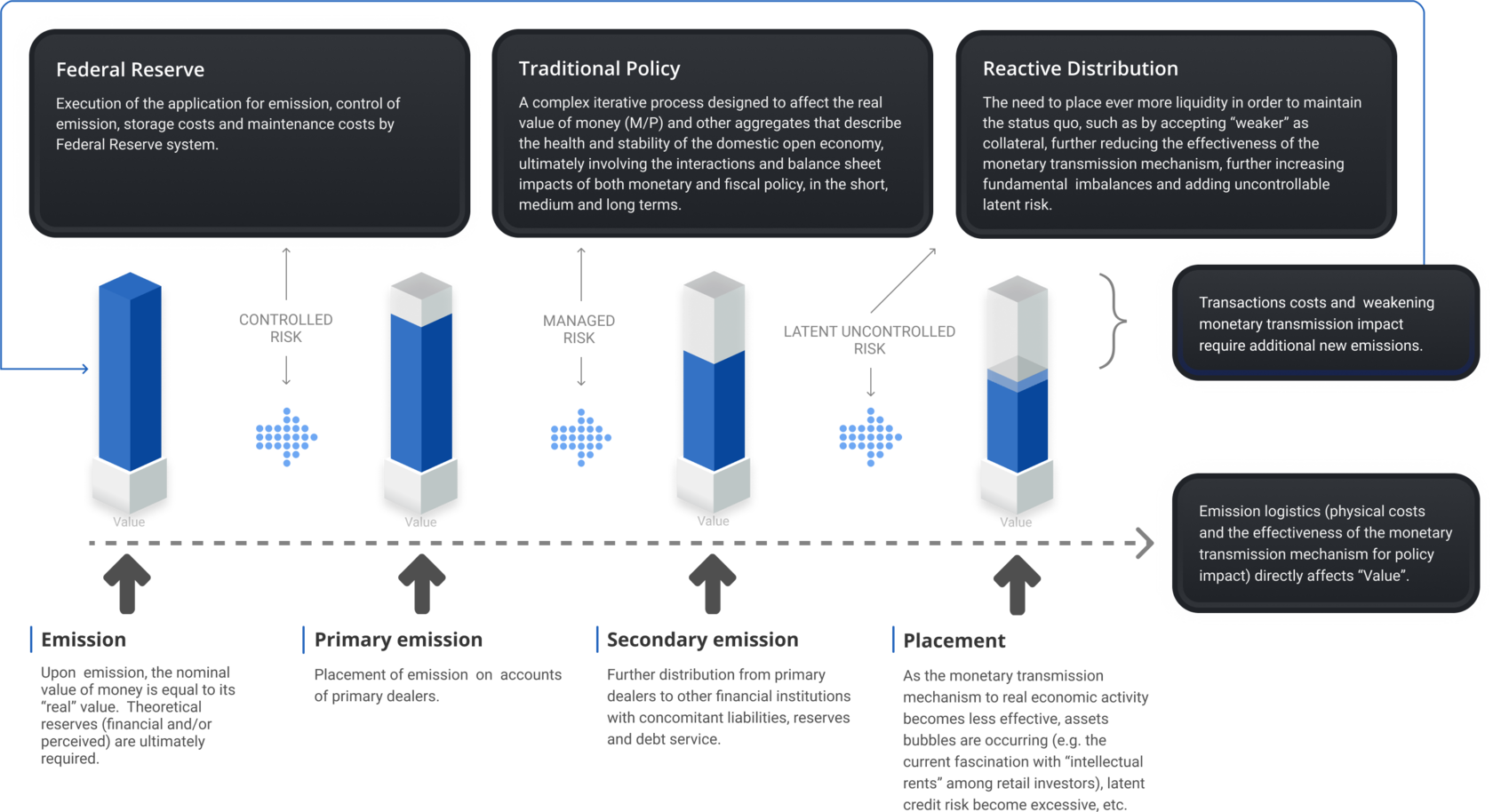
Partial Analysis of Paralysis
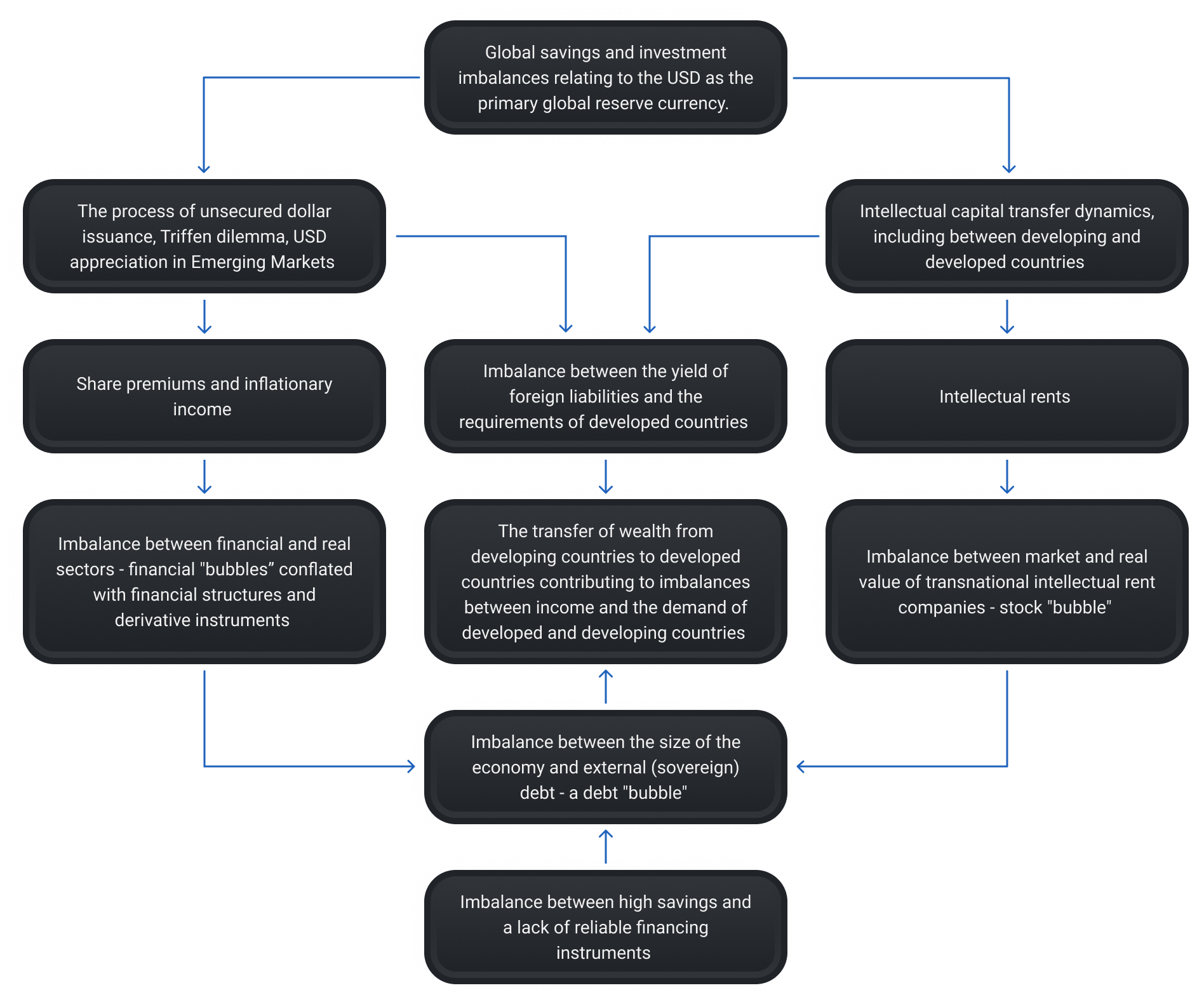
Imbalance in the functions of the dollar as a national and world currency:
Non-recursive Balance of Payments
Lower GDP Growth
Inflation in commodity markets
Monetary policy transmission efficacy and service value of money erosion
Imbalance between income and consumption:
Mismatch between consumption level and sustainable disposable income
Trade deficits and financial surpluses (and visa versa) that may be non-optimal with regard to global productivity
Imbalance between the size of the financial and real sectors:
Traditional (e.g., corporate) risk assessment methods protect against but do not gauge systemic failures
Pumping liquidity to mitigate the crisis and stimulate demand
Growth of off-balance sheet liabilities - derivatives, hedge funds (prime brokerage behavior), etc.
Imbalance between market and real value of corporations:
Ruin cycles of entire sectors of the economy encouraged by "disruptive technology" companies' over-valuation
Violation of sound banking; e.g., debt/EBIDTA, debt/equity, currency exposure
Building demand for:
Better global monetary system of exchange;
Better intrinsic benchmarks for value assessment and practice;
Revival of the functions of money;
Revival of the efficacy of the monetary transmission mechanisms
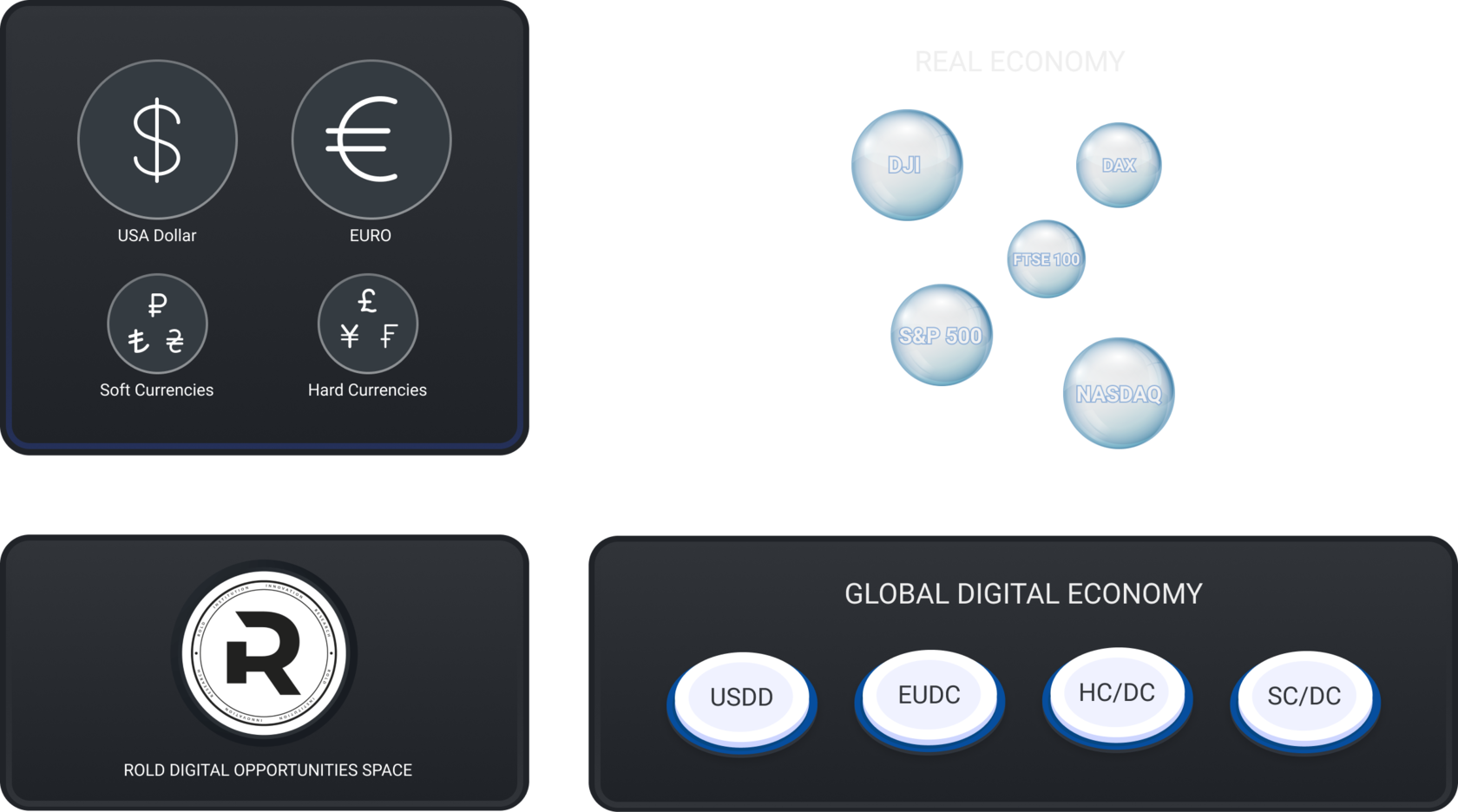
Current Digital / Crypto Market Structure in Relation to Fiat
The crypto market is detached from the fundamentals of the real economy, and to date has minimal impact on finance and payment systems.
Stable Coins are essentially commercial digital money, limited by the available funds on the account of the issuing companies, and as a rule these companies are not audited.
The crypto market operates in parallel with the fiat market - their relationship is based on "Stable Coins".
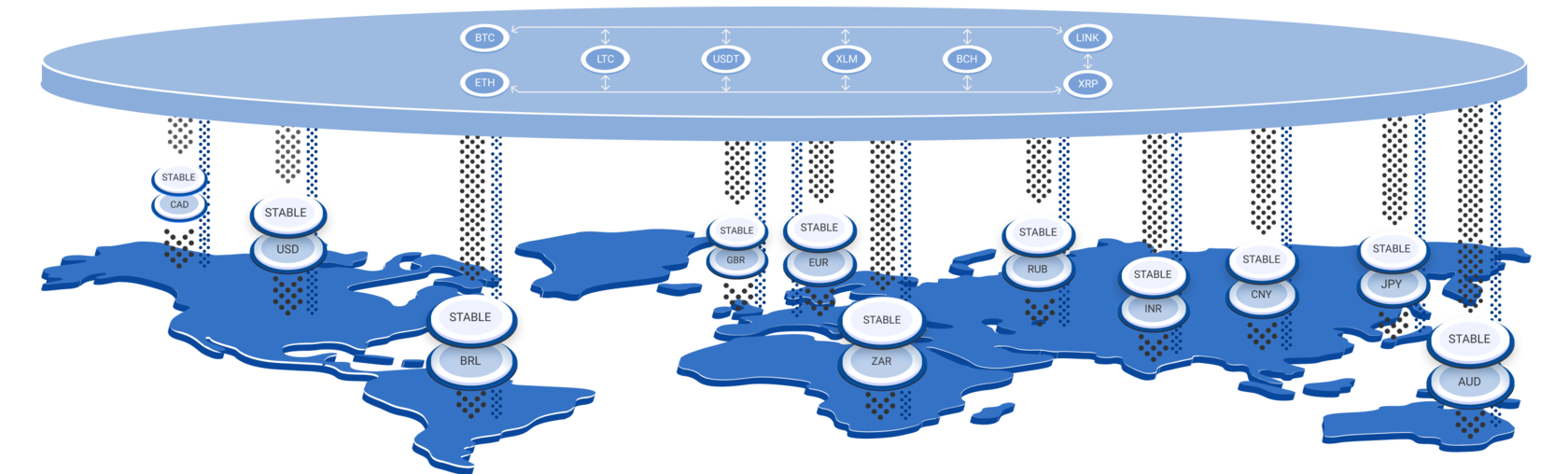
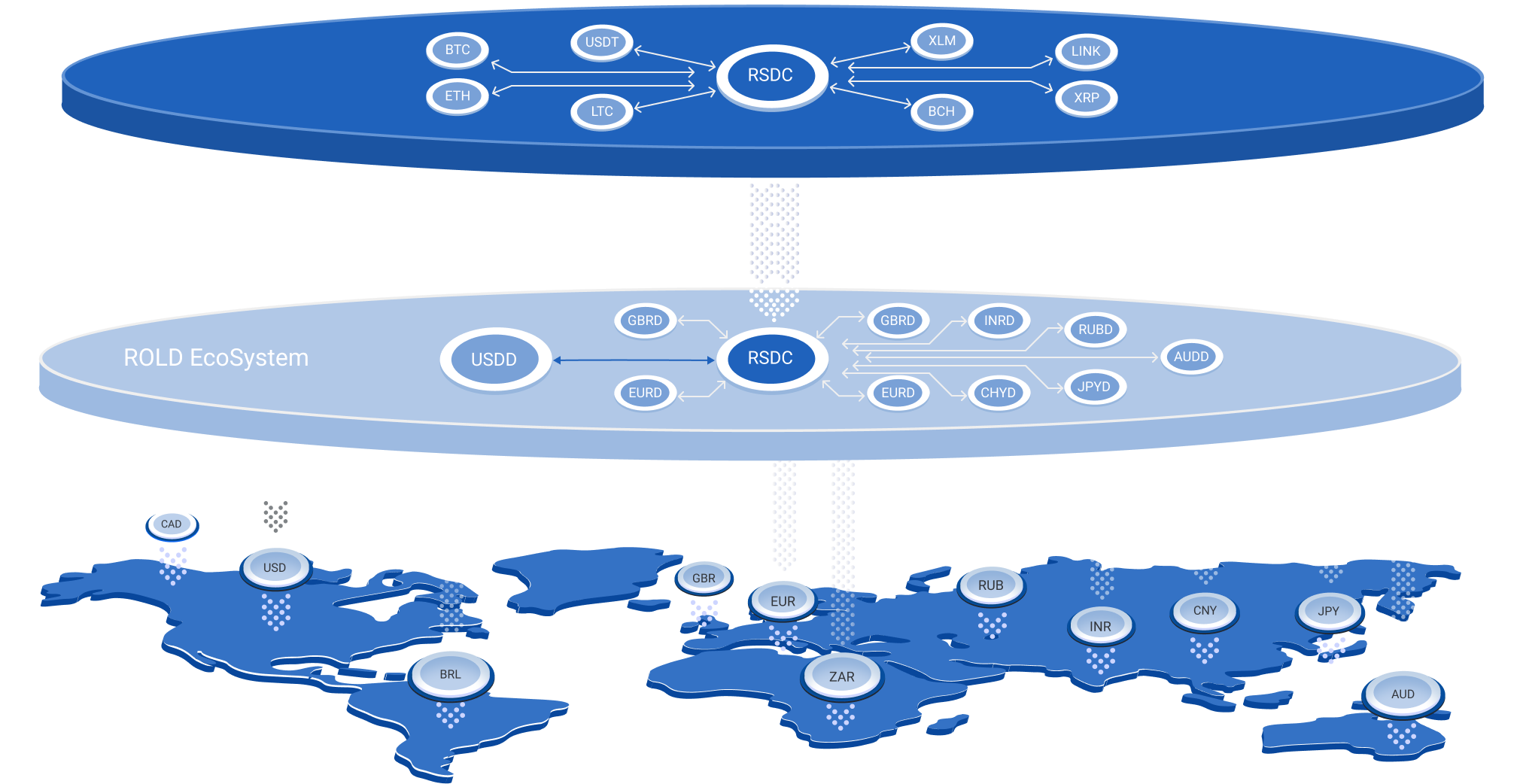
How does ROLD work?
ROLD proprietary language and operational facilities decentralize the emission system and confirmation process through an open language and operational interface, while centralizing a balanced institutional leger and control system in digital format supported by appropriate legal agreements.
ROLD's unique core-chain digital technology allows any qualifying sovereign, financial institution and/or crypto agent to digitally interface with ROLD, subject to counter-parties accepting "rules of the game" regulated by each other. Ultimately, sovereign issuers will define the regulatory rules of the game, to be accepted by counterparts on a voluntary basis.
The ROLD EcoSystem includes a full range of monetary emission (for sovereigns), banking, wallet and exchange services, in both fiat and digital formats.
Through rules of the game, ROLD allows issuers to underwrite assets of intrinsic value less than nominal value through over-collateralization, and to work with multi-temporal issues, such as futures, forwards and options.
ROLD employs sovereign issuance rights to manage risks represented by sovereign issuance, without sovereigns taking any financial risk associated with ROLD itself, nor with any type of crypto issue risk.
What is RSDC?
Synthetic risk is a convergent tool that meets the properties, qualities and characteristics of both classical monetary (including risk) and cryptographic space entities.
ROLD employs issuance rights, ROLD's proprietary core-chain language "Stellar", and a digitalized leger and control system modelled after the US Federal Reserve and Treasury system, to create, manage and utilize "Synthetic Risk".
ROLD Synthetic Digital Currency (RSDC) is the digital currency manifestation of the ROLD system.
ROLD-RSDC is neither a fiat nor a crypto entity, but rather a tool for creating bilateral risk with any counterparty of a possible pair.
Via Stellar, RSDC is able to interface with any voluntary issuer or buyer.
The RSDC issuance process is seamless, rapid, and comparatively cost-free.
RSDC is not subject to any of the factors that typically affect sovereign risk, such as a country's fiscal policy, regulatory policy, various political pressures, etc.
ROLD-RSDC preserves and uses the conventional system of relationships in the classical world (such as between emission center, emission agent, treasury, market makers and so on).
RSDC is a universal clearing agent and value-hold agent in relation to any digital sovereign emission.
RSDC itself is supported by internal processing from emission to distribution, where use and turnover of any centralized issue does not compromise the sovereignty and rights of the issuer, while minimizing the costs and risks of the issue.
RSDC allows the export and voluntary acceptance of issuer constitutions and regulations.
RSDC is supplemented by a toolkit for crisis, administrative, structure, logistics and financial management.
Most importantly, ROLD-RSDC is not designed to be disruptive - it is designed to advance both the fiat and crypto worlds.
ROLD/RSDC: A new generation of money and risk in digital form
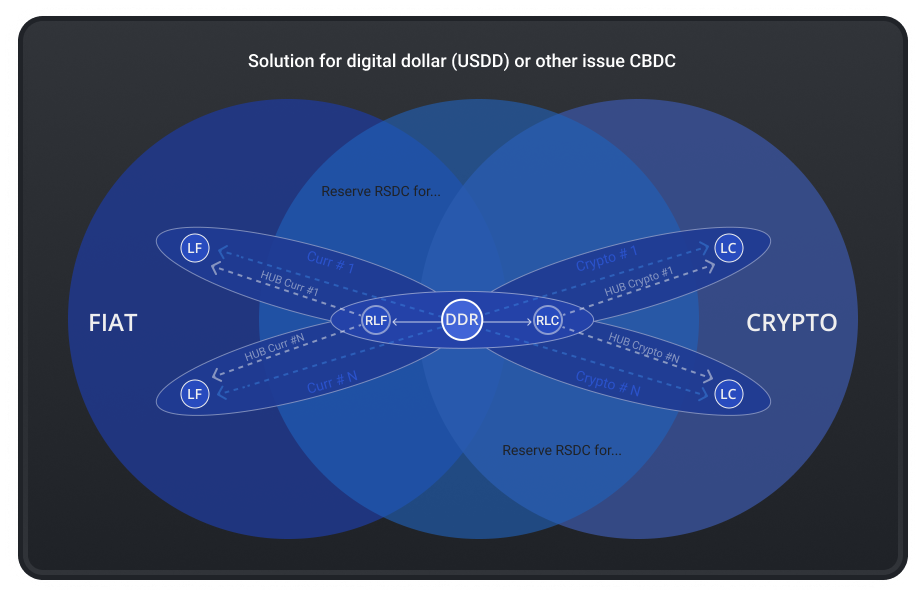
Ecosystem RSDC
LF (for “legal fiat") - legal basis and realization (sale) of the primary emission risk.
RLF (for “regulated legal fiat") - main regulators and aggregators of interaction with the fiat digital environment.
RLС - (for “regulated legal crypto") main regulators and aggregators of interaction with the cryptographic digital environment.
RLF (for “regulated legal fiat") - main regulators and aggregators of interaction with the fiat digital environment.
RLС - (for “regulated legal crypto") main regulators and aggregators of interaction with the cryptographic digital environment.
LC - (for “legal crypto") tools for interacting with the cryptographic digital environment, facilitating an export of regulatory requirements from monetary and financial authorities.
DDR (“for decentralized distribution rules") - rules, rights and obligations of the decentralized distribution model and the application of decentralized distribution and use protocols.
DDR (“for decentralized distribution rules") - rules, rights and obligations of the decentralized distribution model and the application of decentralized distribution and use protocols.
Decomposition characteristics
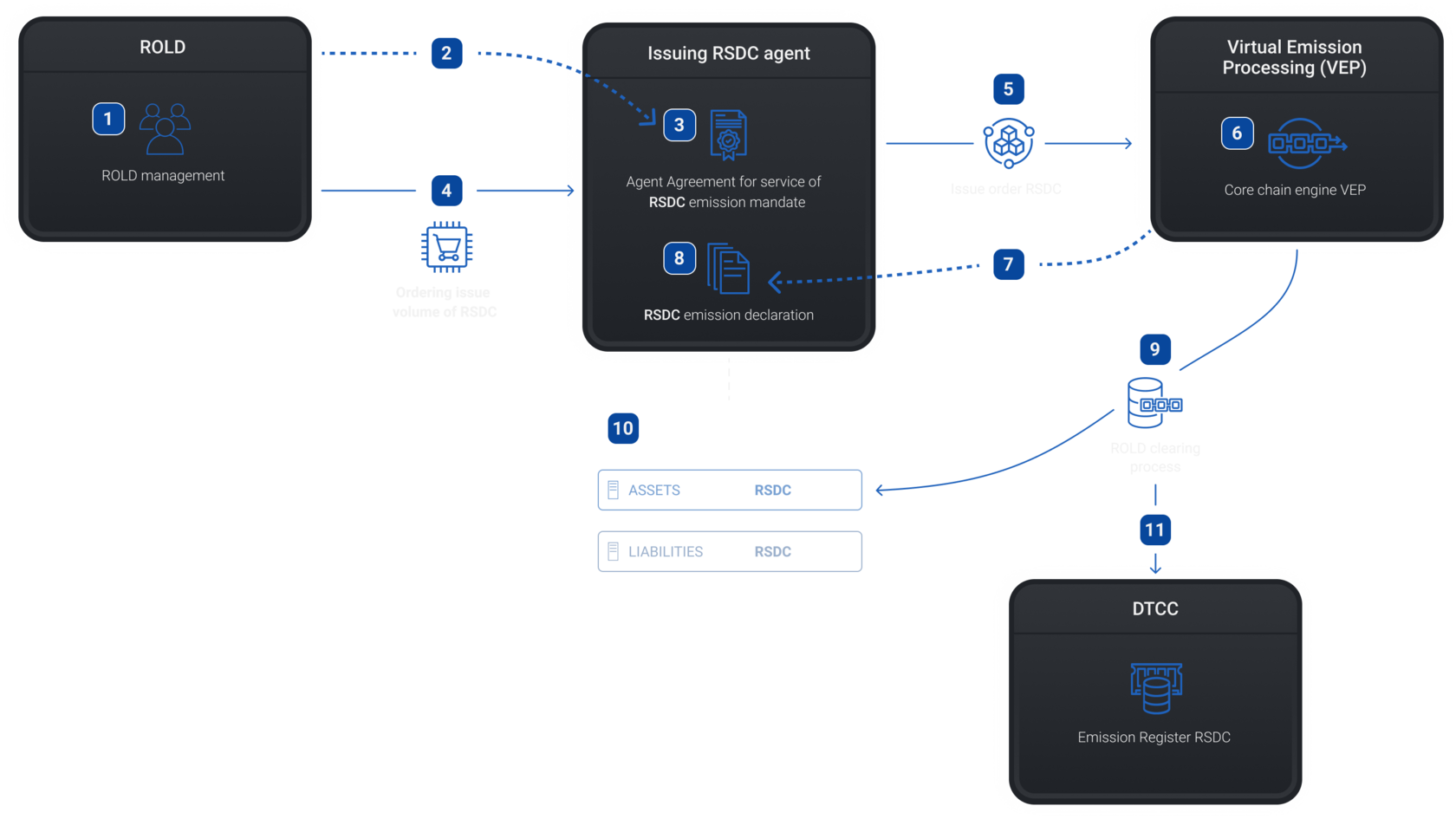
1 - Authorized body: ROLD
2 - Agent Agreement
3 - Agent Agreement corresponds RSDС emission mandate
4 - Ordering issue volume of RSDС
5 - Opening issue order for RSDС
9 - ROLD clearing process - ensures the release of assets using Stellar core chain technology
6 - Virtual Emission Center - provides accounting of issued assets
7 - Asset Issue Status Report
10 - Accounting on the balance sheet of the RSDС issue: ASSETS - amount to turnover;
LIABILITIES - SWAP not limited by the time frame
LIABILITIES - SWAP not limited by the time frame
11 - Formation and redistribution of the emission declaration (USDD)
Emission RSDC
Step 1
8 - RSDС emission declaration
Digital architecture and sketch of meta-algorithm
The series of steps below illustrate the digital-institutional architecture of the ROLD issuance process and system, including multi-nodal control mechanisms to eliminate operational risks.
The steps and sub-steps illustrated below are a minimal sketch of the meta-algorithm, and sub-algorithms.
The steps and sub-steps illustrated below are a minimal sketch of the meta-algorithm, and sub-algorithms.
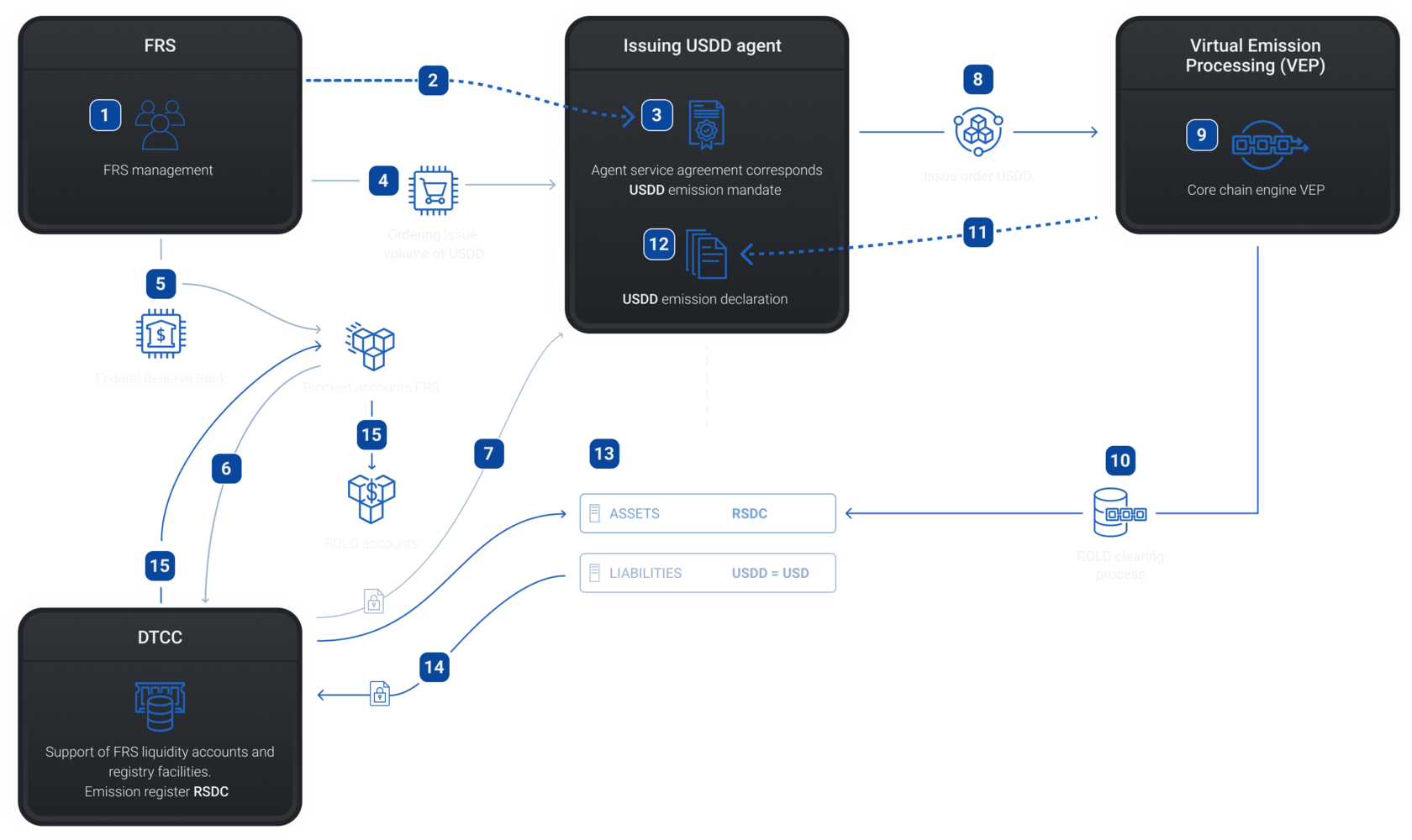
1 - Federal Reserve System
2 - Legal relationship between FRS and emission management agent (USDD)
3 - Agreement corresponds USDD emission mandate
4 - Ordering issue volume of USDD
7 - Obtaining information from clearing company about the presence of collateral on the FRS accounts
5 - Correspondence of collateral amounts to blocked FRS Accounts
6 - Obtaining information by clearing company about presence of collateral amounts
8 - Opening an issue order for USDD
Accounting USDD
Step 2
9 - Virtual Emission Center - provides accounting of issued assets
10 - ROLD clearing process - ensures the release of assets using Stellar core chain technology
11 - Asset Issue Status Report
12 - USDD emission declaration
13 - Accounting on the balance sheet of the USDD issue: ASSETS - amount to turnover; LIABILITIES - SWAP not limited by the time frame
15 - Transfer to accounts of ROLD Institute of service charges
14 - Application to clearing company for issue and registration of specified volume of USDD
1 - Federal Reserve System
2 - Agent draft of volume USDD emission
3 - Correspondent sub-sovereign right declaration and approval
6 - The core of the process of moving currency into the blockchain
9 - Accounting for the received assets of USDD and liabilities in the form of emission risk
7 - Accounting for the received assets of RSDС and liabilities in the form of emission risk
8 - Swap operation for the exchange of assets at a fixed rate and the formulation of open positions
10 - Connection and data transmission over a secure channel (DTCC)
First emission RSDС
Step 3
4 - Agent service agreement corresponds RSDС emission mandate
5 - Sub-sovereign emission right confirmation
11 - ROLD Institution accounting of liquidity reserve upon correspondent bank account in USD as well as reserved register in DTCC
12 - Bank account operations
1 - Federal Reserve System
2 - Agent draft of volume USDD emission
3 - Correspondent sub-sovereign right declaration and approval
5 - ROLD clearing processing
9 - Connection and data transmission over a secure channel (DTCC)
6 - Accounts agent distribution of RSDC
7 - Exchange engine
10 - Accounting balance sheet
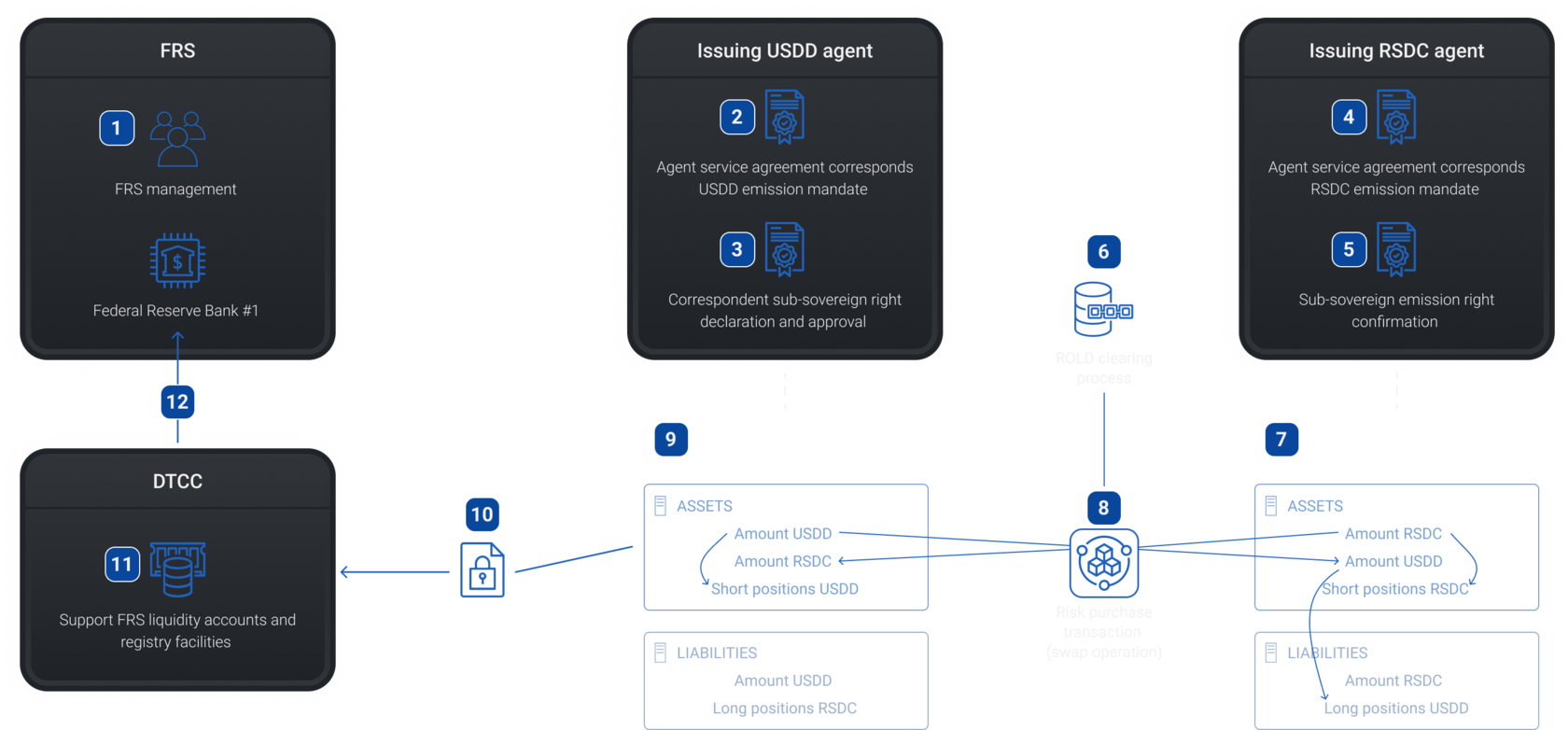
Secondary emission of RSDC through distribution agents
Step 4
4 - Agent service agreement corresponds RSDС emission mandate
11 - Operations of banks account
8 - Balance sheet - short and long position
1 - Federal Reserve System
2 - Agent draft of volume USDD emission
3 - Correspondent sub-sovereign right declaration and approval
5 - Sub-sovereign emission right confirmation
9 - Balance sheet of USDD agent
6 - ROLD clearing process
7 - Balance sheet of USDD agent
10 - Connection and data transmission over a secure channel (DTCC)
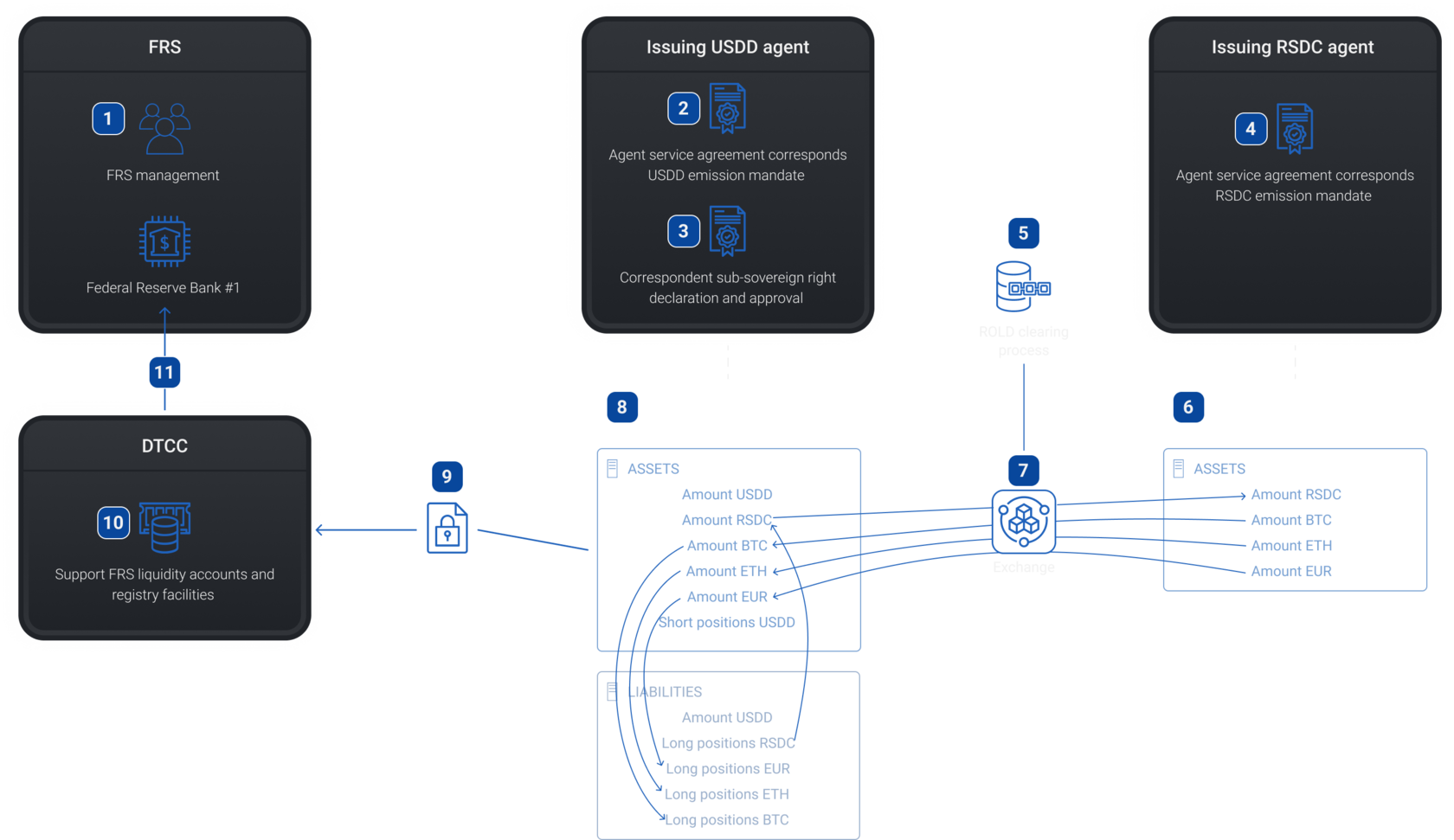
Formulation of income items by USDD agent
Step 5
4 - Agent service agreement corresponds RSDС emission mandate
11 - Accounting balance sheet
8 - Exchange engine
12 - Operations of banks account
1 - Federal Reserve System
2 - Agent draft of volume USDD emission
3 - Correspondent sub-sovereign right declaration and approval
5 - Sub-sovereign emission right confirmation
9 - The holder of the RSDC conducts the posting to FIAT
6 - ROLD clearing process
7 - Balance sheet of RSDC agent
10 - Balance sheet of USDD agent
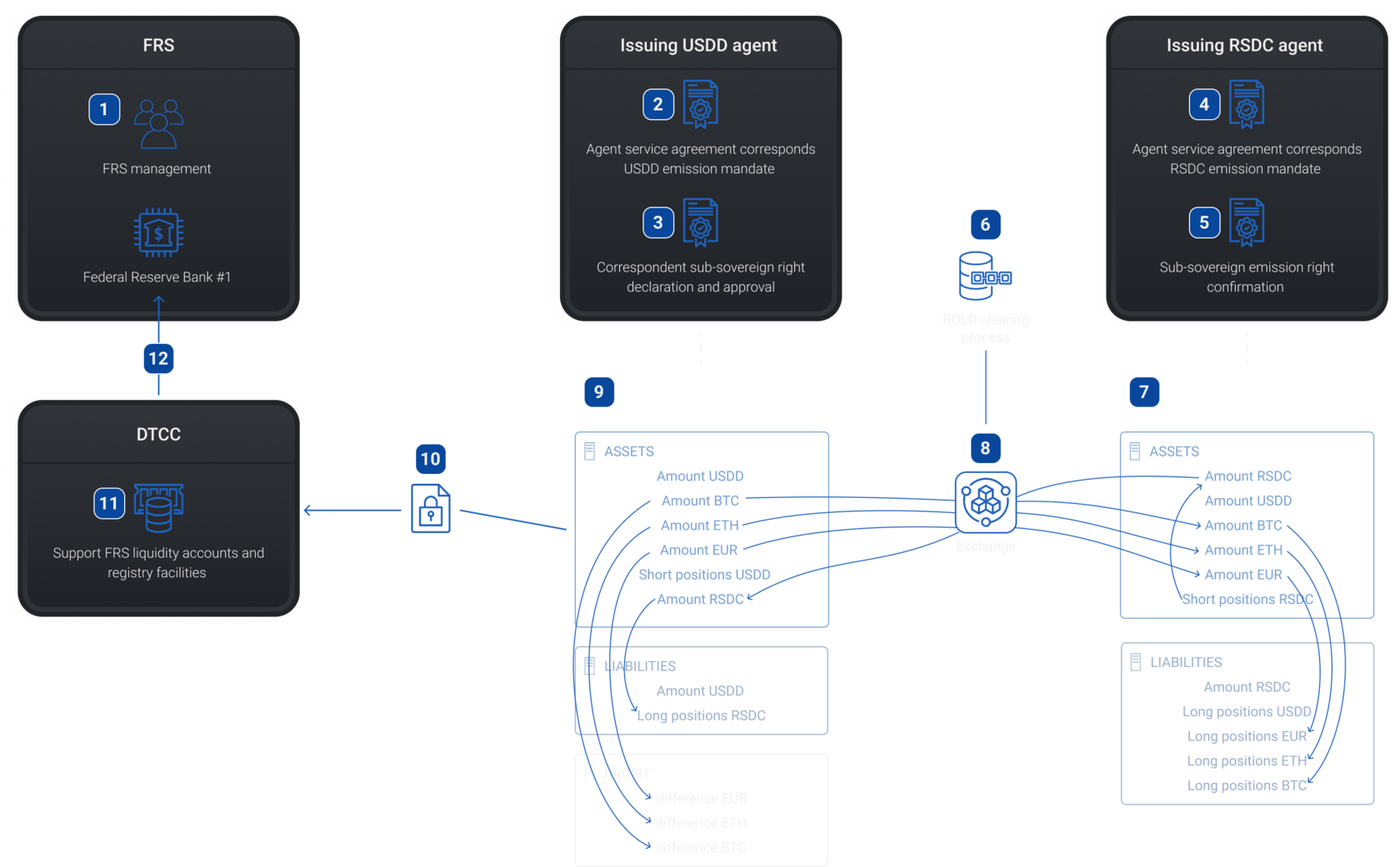
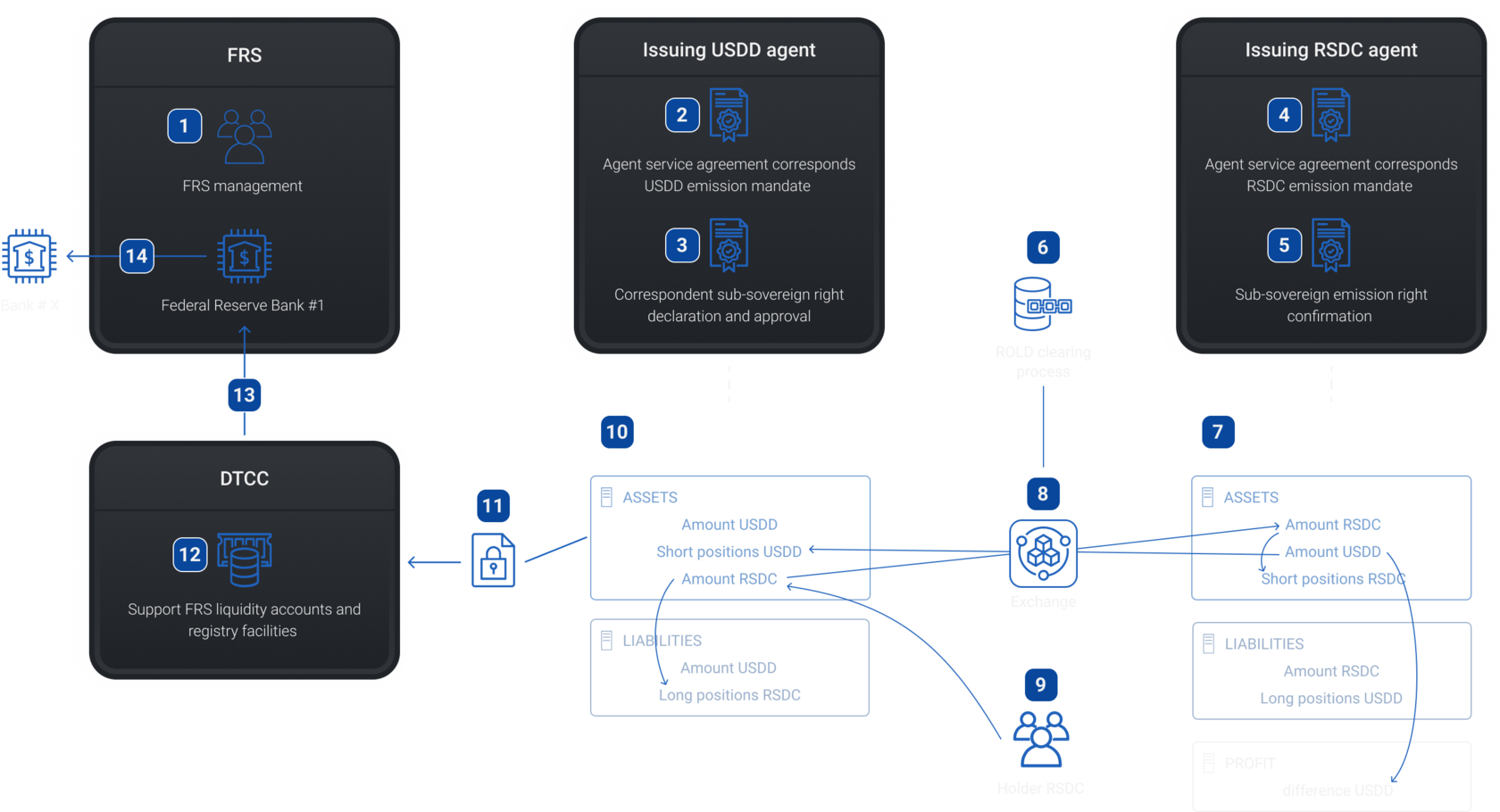
Formulation of income items by RSDC agent
Step 6
4 - Agent service agreement corresponds RSDС emission mandate
11 - Connection and data transmission over a secure channel (DTCC)
8 - Exchange engine
12 - Accounting balance sheet (USDD)
13 - Operations of bank accounts (USDD)
14 - Operation to ROLD Institution's digital wallet (USDD) or bank account (USD)
Introduction to ROLD
Acceleration of digital technology and evolution of the global economy call for adaptation of the architecture of the monetary emission processes. While pressuring the classical system, the digital economy also represents an opportunity to establish an advanced monetary emissions process to improve efficiency of turnover, better encourage productivity and wealth generation, and better manage risks and crises. The classical monetary system will need to evolve to remain relevant. As we shall describe below, a key to success will be to achieve a digital diversification of the emission process, while maintaining core features of the Classical system.
Modern Classical monetary systems are becoming "declassified" in the sense that practice has outpaced theory. In the presence of rapid, organic, technological and financial-structural advancements of monetary-financial agents, monetary-financial-regulatory de facto policy is generating unidentified and undescribed risks that limit their overall effectiveness, and importantly, their potential for systemic crisis management.
Meanwhile, decentralized emissions of non-centralized issuers in the form of digital entities based on cryptography and mathematics has led to fundamental tensions (including challenges to sovereignty) between classical centralized money emission institutions and the jurisdiction-free, quasi-monetary environment of "surrogate-decentralized" turnover outside the bounds of regulations, collateral and liquidity.
Modern classical monetary responses to crises (and avoidance thereof) are threatening longer run sustainability of the global economy. Quantitative easing and other monetary tools work to quell recessionary pressures. However, their effectiveness decreases and imbalances increase as they are used to greater and greater extent. The magnitude of latent potential shocks and vicious cycles are cumulative and may well be exponential. The role of derivatives and financial structured leverage cannot be underestimated, both to the effectiveness of modern classical policy, and to its potential deleterious results.
The classical system is evolving in a worrisome way for the system itself. The emission policy of the most important money issuers is increasingly different from classical theory and methodology, including a decoupling of fundamentals (financial validity and security) in parallel with a (still) latent erosion of trust, contributing further to the declassification of money as a pronounced value and service script, and increasingly emphasizing money as fuel in support of market liquidity and asset prices.
Modern Classical monetary systems are becoming "declassified" in the sense that practice has outpaced theory. In the presence of rapid, organic, technological and financial-structural advancements of monetary-financial agents, monetary-financial-regulatory de facto policy is generating unidentified and undescribed risks that limit their overall effectiveness, and importantly, their potential for systemic crisis management.
Meanwhile, decentralized emissions of non-centralized issuers in the form of digital entities based on cryptography and mathematics has led to fundamental tensions (including challenges to sovereignty) between classical centralized money emission institutions and the jurisdiction-free, quasi-monetary environment of "surrogate-decentralized" turnover outside the bounds of regulations, collateral and liquidity.
Modern classical monetary responses to crises (and avoidance thereof) are threatening longer run sustainability of the global economy. Quantitative easing and other monetary tools work to quell recessionary pressures. However, their effectiveness decreases and imbalances increase as they are used to greater and greater extent. The magnitude of latent potential shocks and vicious cycles are cumulative and may well be exponential. The role of derivatives and financial structured leverage cannot be underestimated, both to the effectiveness of modern classical policy, and to its potential deleterious results.
The classical system is evolving in a worrisome way for the system itself. The emission policy of the most important money issuers is increasingly different from classical theory and methodology, including a decoupling of fundamentals (financial validity and security) in parallel with a (still) latent erosion of trust, contributing further to the declassification of money as a pronounced value and service script, and increasingly emphasizing money as fuel in support of market liquidity and asset prices.
Sovereign money emission institutions are starting to respond to the digital opportunity. However, they are not well suited to establish and organize decentralized distribution networks. While some bilateral sovereign agreements are taking place, a global standard among them will not be agreed quickly.
Any new global standard (de jure) will only result from a long process of a competitive gaming, negotiation and compromise, given that each sovereign has its own sovereign-exportation goals. In the meantime, individual sovereign emission institutions are attempting to implement their own non-interfacing digital issue avatars, using centralized direct equivalence clearing employing their own digital issue block chains.
Block-chain as envisaged by its original designers (and most users in monetary spheres), invokes decentralized network protocols and facilities - validity is compromised when the chain is centrally managed. This fundamentally leads to a conflict between the regulatory and legal interests of sovereign issuers, and the validity and accessibility of the ultimate possible uses of these emissions.
As a result, the development of sovereign digital money is facing a theoretical and manifest conflict between centralized emission and demand for decentralized forms of monetary clearing and turnover.
Any new global standard (de jure) will only result from a long process of a competitive gaming, negotiation and compromise, given that each sovereign has its own sovereign-exportation goals. In the meantime, individual sovereign emission institutions are attempting to implement their own non-interfacing digital issue avatars, using centralized direct equivalence clearing employing their own digital issue block chains.
Block-chain as envisaged by its original designers (and most users in monetary spheres), invokes decentralized network protocols and facilities - validity is compromised when the chain is centrally managed. This fundamentally leads to a conflict between the regulatory and legal interests of sovereign issuers, and the validity and accessibility of the ultimate possible uses of these emissions.
As a result, the development of sovereign digital money is facing a theoretical and manifest conflict between centralized emission and demand for decentralized forms of monetary clearing and turnover.
Despite efforts, until now, it has proved impossible to export the regulatory and legal norms of the world of fiat currencies into the world of cryptographic entities, leading to a persistent conflict between monetary, regulatory and fiscal institutions and residents of crypto space. The strategy of pressure and forced implementation of the regulatory norms of the fiat world, and their subsequent export, just encourages a further shading of the crypto space and its turnover, and concomitantly limits liquidity.
Forgone benefits of a highly efficient digital system represent lost opportunity. First, significant existent money demand is not being accessed by sovereign suppliers. Second, the digital world has the potential to deliver dramatic productivity increases and cost reductions of the services of money, as well as multiplier effects on other aggregates. Third, a plethora of unqualified investors with too little knowledge and limited opportunities are increasingly oriented in favor of populist solutions of a speculative nature. A decrease in the level of confidence in fiat, as well as the associated risks of loss of savings and capital in light of the Modern Classical policy, lead to an increase in the number of potential crypto space residents.
Situational observations and analysis show a net increase in the number of crypto space residents, and that the level of liquidity associated with this space is also increasing. At the same time, the reaction of the crypto community to attempts to create and distribute centralized digital emission sovereign money remains solidly negative. The main negative reactions are based on fear of suppression and a blockage of free crypto emission, trading and usage, along with a general distrust of the current system of money provision outlined above. This conflict has a negative tendency, and may well result in effective rejection of centralized digital money and turnover absorption.
In short, the crypto community perceives digital money of centralized sovereign issuers as "digitized", but not "digital fiat money" that meet the demand of crypto space residents.
Forgone benefits of a highly efficient digital system represent lost opportunity. First, significant existent money demand is not being accessed by sovereign suppliers. Second, the digital world has the potential to deliver dramatic productivity increases and cost reductions of the services of money, as well as multiplier effects on other aggregates. Third, a plethora of unqualified investors with too little knowledge and limited opportunities are increasingly oriented in favor of populist solutions of a speculative nature. A decrease in the level of confidence in fiat, as well as the associated risks of loss of savings and capital in light of the Modern Classical policy, lead to an increase in the number of potential crypto space residents.
Situational observations and analysis show a net increase in the number of crypto space residents, and that the level of liquidity associated with this space is also increasing. At the same time, the reaction of the crypto community to attempts to create and distribute centralized digital emission sovereign money remains solidly negative. The main negative reactions are based on fear of suppression and a blockage of free crypto emission, trading and usage, along with a general distrust of the current system of money provision outlined above. This conflict has a negative tendency, and may well result in effective rejection of centralized digital money and turnover absorption.
In short, the crypto community perceives digital money of centralized sovereign issuers as "digitized", but not "digital fiat money" that meet the demand of crypto space residents.
The solution to this "centralized – decentralized dilemma" is a new generation of risk emission – specifically, in the form of "Synthetic Risk". Synthetic risk is a convergent tool that meets the properties, qualities and characteristics of both classical monetary (including risk) and cryptographic space entities. We have named this next generation synthetic risk, ROLD, and in digital format - Rold Synthetic Digital Currency (RSDC).
Rold-RSDC represent a unique system environment, integrating fiat and crypto on an equal basis. Rold-RSDC allows for the construction of a system of simultaneous centralized emission actions, and a decentralized system of risk management, confirmation and distribution, by maintaining the principle of centralization in respect to rights and obligations, including at the systemic, administrative and financial levels, while facilitating the use of protocols and procedures required for the interaction of targeted formats with decentralized systems, including via block chain.
The digital-money-emission model is represented by basic monetary principles, rules and regulations, established through rigorous mathematic principles and regulated procedures in digital space. The architecture of the system is equally correct for classical monetary emission practices and for new generation digital emission and usage.
Importantly, the model invokes universal digital capabilities where every centralized issuer is entitled to the implementation and use of emission and clearing with third-party issuers and users, while establishing constitutional and regulatory frameworks, which do not compromise sovereign emission rights, nor involuntary crypto freedoms. Crypto issuers and users effectively and voluntarily sign up to counterparty (typically sovereign) rules of the game.
Rold-RSDC represent a unique system environment, integrating fiat and crypto on an equal basis. Rold-RSDC allows for the construction of a system of simultaneous centralized emission actions, and a decentralized system of risk management, confirmation and distribution, by maintaining the principle of centralization in respect to rights and obligations, including at the systemic, administrative and financial levels, while facilitating the use of protocols and procedures required for the interaction of targeted formats with decentralized systems, including via block chain.
The digital-money-emission model is represented by basic monetary principles, rules and regulations, established through rigorous mathematic principles and regulated procedures in digital space. The architecture of the system is equally correct for classical monetary emission practices and for new generation digital emission and usage.
Importantly, the model invokes universal digital capabilities where every centralized issuer is entitled to the implementation and use of emission and clearing with third-party issuers and users, while establishing constitutional and regulatory frameworks, which do not compromise sovereign emission rights, nor involuntary crypto freedoms. Crypto issuers and users effectively and voluntarily sign up to counterparty (typically sovereign) rules of the game.
Live example of listing Rold (RSDC) on an exchange and establishing a value in terms of Bitcoin
DIGITAL OPPORTUNITY SPACE
Employing classical monetary emission in the digital space
The main digital capabilities are as follows
Emission
Custodian
Trust and Management
Clearing
The ROLD Space of the Digital Opportunities is secure and effective for classical monetary emission clearing in digital form. ROLD's architecture delivers process and legal/regulatory capabilities to enable smooth functioning of trust-clearing hubs, creating all prerequisites for implementation of classical emission clearing in the digital space.
The digital currency of the system is a vector subsuming multifunctional provision. It contains the characteristics of money as well as the necessary qualities of a clearing agent, including a legitimate level of authority and its own value. ROLD Ecosystem supporting proprietary software and institutional process capabilities enable multiple and simultaneous valence relationships. Seamless digital operations offer the opportunity to maximize financial results with minimal operational and currency risks. Accessing the digital currency world on a mutually accepted regulatory basis creates conditions for the most efficient use of digital currencies of different classifications.
The digital currency of the system is a vector subsuming multifunctional provision. It contains the characteristics of money as well as the necessary qualities of a clearing agent, including a legitimate level of authority and its own value. ROLD Ecosystem supporting proprietary software and institutional process capabilities enable multiple and simultaneous valence relationships. Seamless digital operations offer the opportunity to maximize financial results with minimal operational and currency risks. Accessing the digital currency world on a mutually accepted regulatory basis creates conditions for the most efficient use of digital currencies of different classifications.
Basic principles of relationships
Centralized Issuer (central banks and/or their authorized institute) enters into an Agent Contract with the ROLD Institute.
The goal is to provide and implement CBDC emission capabilities, create and implement risk management, and ultimately operationalize use and clearing capabilities with other digital entities, including, but not limited to, third party issue CBDC.
The Institute performs all necessary operational and regulatory functions as a service provider to counterparties, including acting as Emission Agent, Management Agent, and Clearing Agent.
1
2
3
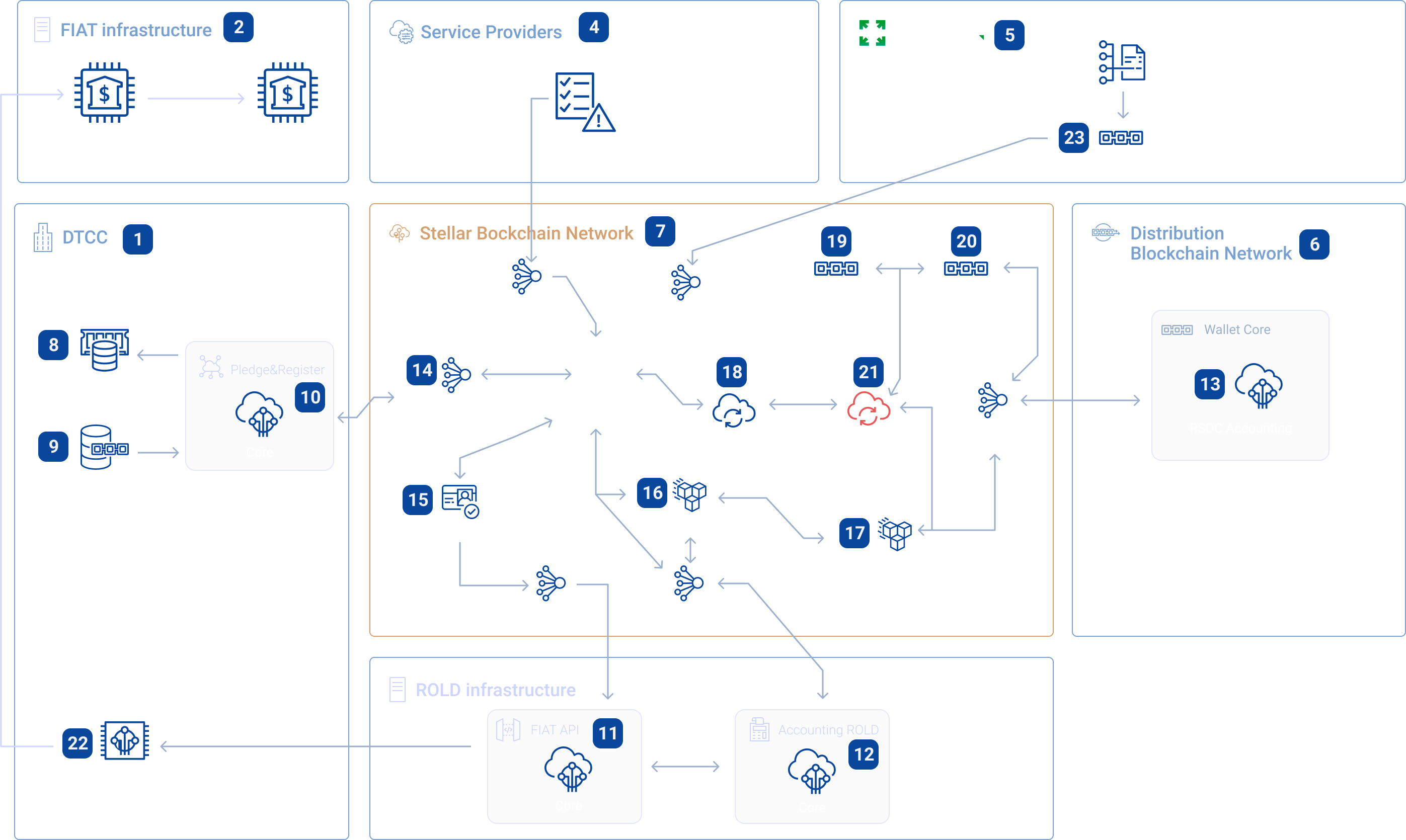
The ROLD virtual issuing machine (hereinafter VEM) is a program complex that performs the functions of centralized emission and processing of RSDC asset turnover operations.
High-level process, describing the interactions of the modules of the Virtual Emission Machine
General scheme
ROLD Virtual Emission Machine
VEM consists of four separately function software packages:
Main Software Modules
Pledge&Register (number 10) - a software module located within the infrastructure of the companies that maintain ROLD accounts in FIAT and carry out clearing operations at the request of ROLD. The main functionality of the software package is the receipt and maintenance of the register issued by RSDC under the security of FIAT assets (received from the Stellar network) and transmission of information about the state of the FIAT asset accounts to the Stellar network, for further displaying information about the security in the Wallet Core software package (number 13). Pedge&Register uses the Stellar network as a medium for transferring and storing information, but does not require connection with the ROLD infrastructure.
FIAT API (number 11) - a software package that transfers commands to a clearing company for conducting operations with FIAT. It operates according to the rules of the clearing company and is part of the ROLD infrastructure. With the development of RSDC, it will be possible to switch to the maintenance of the wallet within the infrastructure of the clearing company in the digitized form of the FIAT asset.
Accounting ROLD (number 12) - a software package responsible for transferring commands from the Stellar network into the FIAT gateway of a clearing company, including account maintenance, accounting, and transactions monitoring. It is the accounting and processing part of VEM and an integral part of the ROLD infrastructure.
Wallet Core (number 13) – This is a custom kernel performing client operations with RSDC, acting as a complete repository of the state of the Stellar network. It facilitates RSDC transition between distribution networks, providing information about the provision and the aggregate state of the user's KYC. It is used by both individual users and maintainers of RSDC nodes.
VEM Providers and Users
VEM providers and users fall into the following functional categories:
Clearing companies (number 1) - clearing companies and / or banking organizations that maintain ROLD accounts in FIAT assets and clear ROLD's operations in FIAT assets. They perform the following basic atomic functions: maintaining accounts in FIAT (number 8), maintaining RSDC issue registers for accounting operations (number 9), and provide a full range of operations in the FIAT asset (number 22)
Banking institutions (number 2) – They carry out transactions in the FIAT infrastructure and can perform clearing operations for ROLD.
ROLD Company (number 3) – ROLD's settlement complex, which performs the functions of accounting for transactions in RSDC.
Service providers (number 4) - Certified companies, with the necessary licenses, providing VEM with the necessary accompanying business processes within their competencies and information capabilities, such as KYC & AML (number 15) of RSDC holders to enable the transition to FIAT operations.
KYRREX Company (number 5) - a company that provides information on the market value of RSDC in relation to other assets, both crypto and FIAT. Is a wholesale distributor of RSDC. It delivers market quotes to VEM using the Stellar node (number 23).
RSDC Holders (number 6) - Wallets of RSDC holders in various distribution networks. They carry out transactions of RSDC turnover, being the main consumers of the asset.
VEM Protocols
VEM exploits Stellar blockchain capabilities (number 7) to carry out issuing and processing operations using the following protocols:
Stellar Network Connection Protocol (number 14) - a set of methods for interaction between the Stellar network and external software systems, based on the methods, procedures, functions and internal protocols of the Stellar network.
KYC & AML Protocol (number 15) - Stellar network protocol providing the functionality of KYC & AML processes of RSDC holders to provide access to operations in FIAT. Requires connections to service providers.
Emission Protocol (number 16) - an internal protocol of the Stellar network that provides the processes of issuing RSDC and accounting units such as USDD, EURD, etc.
Emission Distributive Network Protocol (number 17) - RSDC issuance and accounting protocol in various distribution networks, for example ETH.
Exchange Protocol (for example 18) An internal protocol of the Stellar network that performs asset exchange transactions using Stellar's calculated capacity.
Account Asset Freeze (number 19) - A protocol for maintaining accounts that act as a repository outside the operating balances of assets.
Account Asset Distribution Network (number 20) - A protocol for maintaining accounts that acts as a repository of RSDC accounting units in distribution networks.
Asset Exchange Protocol (number 21) - An internal protocol of the Stellar network that handles asset exchange transactions using Stellar's settlement capacity.
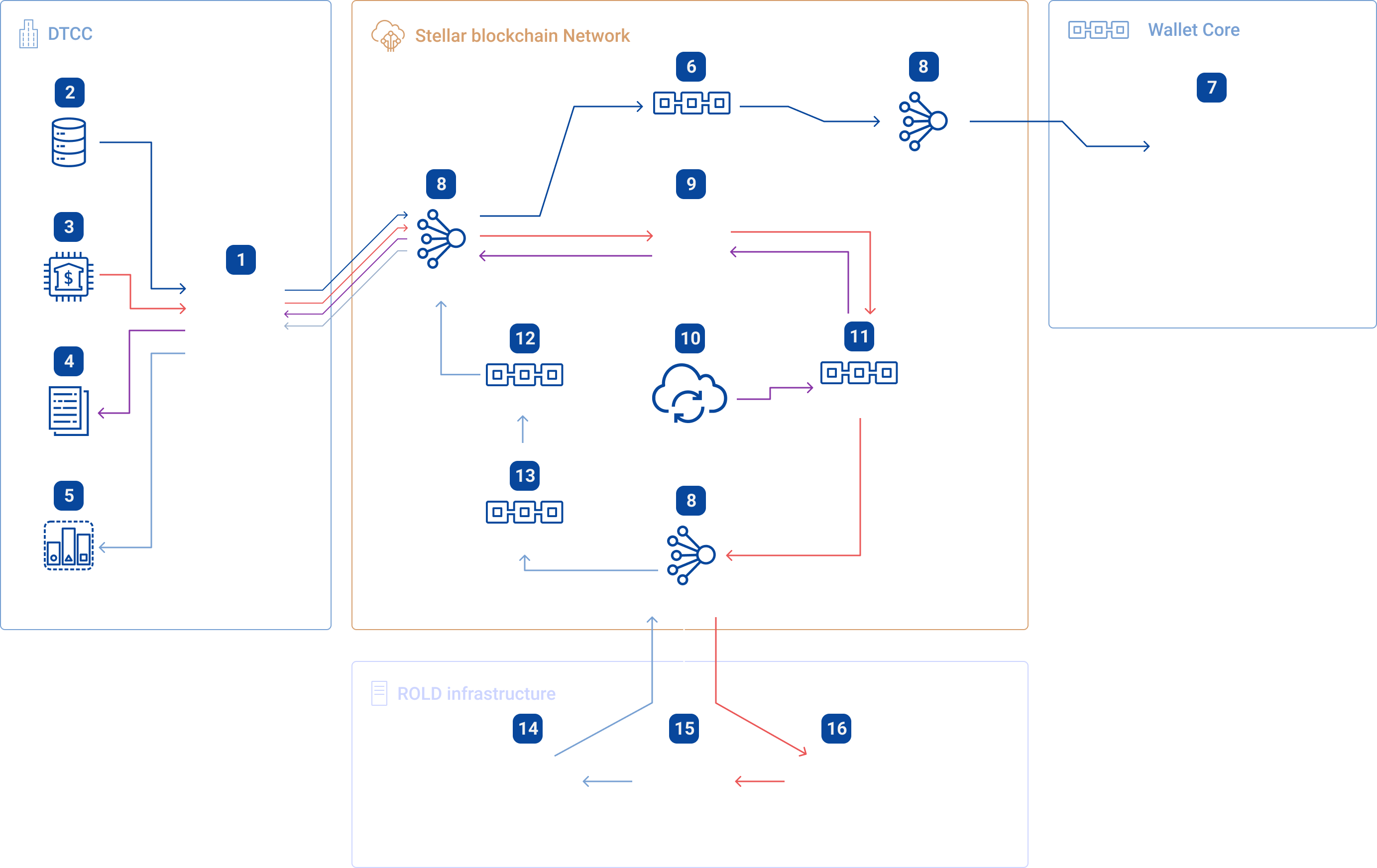
Pledge&Register processing module facilitates the following:
High-level process VEM related to the pledge processing module and the issuance of new receipts.
Module Pledge&Register
Pledge&Register Module
A software module located within the infrastructure of companies that maintain ROLD accounts in FIAT assets and carry out clearing operations at the request of ROLD. The main functionality of the software package is the receipt and maintenance of the register issued by RSDC under the security of the FIAT asset (received from the Stellar network), and transferring information about the state of the FIAT asset accounts to the Stellar network, for further displaying information about the software in the Wallet Core software package. Uses the Stellar network as a medium for transferring and storing information does not require direct communication with the ROLD infrastructure.
Processing and additional issue of RSDC upon receipt of new collateral (number 3) - Information is transferred to the issue protocol (number 9), which conducts USDD issue operations (number 11) and further transfers information to the ROLD infrastructure (number 16), where fair value is calculated RSDC / USDD (number 15), and information is then transmitted to the Stellar blockchain about the RSDC / USDD asset exchange (number 10 and number 14). Through the issue protocol, DTCC receives information about the USDD issue register as collateral (number 4), and the accumulative state of RSDC on the accounts of holders (number 5). The movement of assets occurs through the DTCC account (number 12) and the ROLD Company account (number 13) in the Stellar network.
Connection to the Stellar network is made according to Stellar protocols
(number 8).
(number 8).
For these operations, ROLD Company infrastructure and the DTCC clearing center are not directlyi
connected - the Stellar network acts as a bus (gateway), and security of the connection is ensured by the parties independently, in accordance with security protocols in force in the participating companies.
connected - the Stellar network acts as a bus (gateway), and security of the connection is ensured by the parties independently, in accordance with security protocols in force in the participating companies.
Processing the status of accounts in FIAT assets owned by ROLD (number 2). Using the Pledge & Register module (number 1), information about the status of accounts is stored in the Stellar blockchain on a special information account (number 6) and transmitted to all network participants, whereby all network members receive online state and status of the collateral in the Wallet Core software package (number 7). The state of the collateral changes according to the condition of the change in the account balances of the ROLD Company in DTCC. The information goes through encryption protocols at the time of writing to the blockchain and decryption by Wallet Core (number 7).
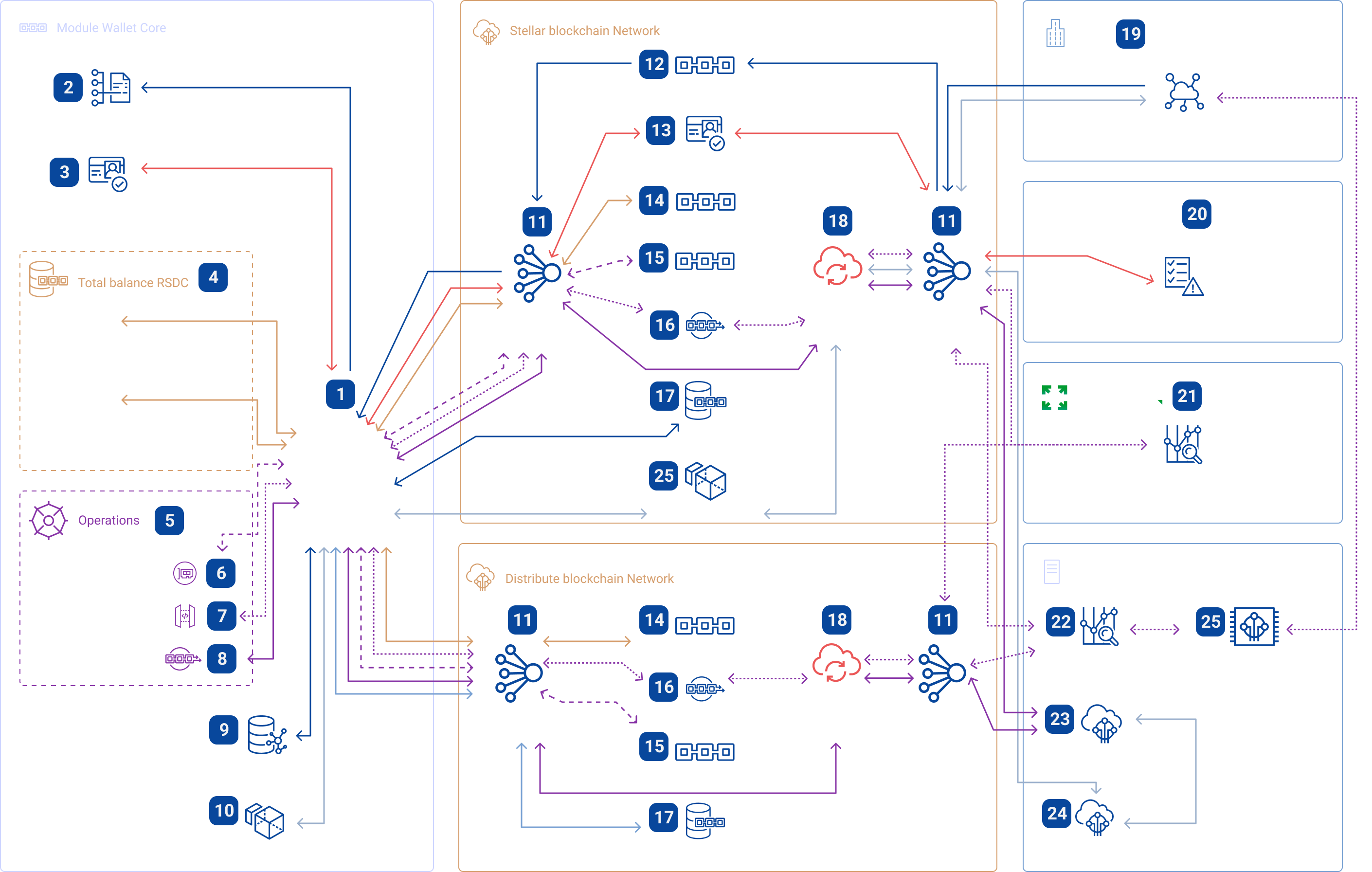
Wallet Core processing module facilities the following:
High-level functionality Wallet Core from retail and instutional customer
Wallet Core
Wallet Core Module
The custom kernel that performs client operations with RSDC acts as a complete repository of the state of the Stellar network. It facilitates RSDC transition between distribution networks, providing information about the provision and the aggregate state of the user's KYC. Both individual users and RSDC node maintenance companies/institutions have use access.
Provision of collateral information - the user receives the status of the collateral in real time (number 2), this is done on the side of the clearing company (number 19) through the account status in the Stellar network (number 12, see above).
Status of the KYC & AML process (number 3) – A user receives status in the RSDC network, which displays the AML status and user verification regardless of the form of ownership. The absence of such a status prohibits the user from going into the FIAT turnover while allowing her to be in the Crypto turnover. The KYC process is carried out through the protocol (number 13), which provides the procedure for connecting with the licensing services provider on the market (number 20).
Offline operations (number 6) – These are carried out between RSDC network users directly between devices that store the token limit using any communication between devices (Bluetooth, IR, cable or printed receipt). To carry out such operations, the user independently creates a token in the system, using the distribution network protocols (number 15).
Users can download the full RSDC network node, which acts as a Wallet
(number 1).
(number 1).
Balances and wallet addresses for different distribution networks (number 4), allow users to review their RSDC balances both in terms of distribution networks and in general. This process is based on receiving information directly from the node of the distribution network from the generated account (number 14).
User operations (number 5) - divided into the following:
On-line transactions (number 7) offer users RSDC network account transfers. Formation of a pool of accounts can be used both for private payments and for commercial ones. Payments are made directly by the distribution network protocol and processing takes place within the network (number 16). If there is a transition to the FIAT circulation network, it is carried out through the asset exchange protocol (number 18), organized in the distribution network, the exchange rate basis is the representative (number 21), the transition to FIAT goes through the ROLD protocols (numbers 22 and 25) when the transaction is transferred to the clearing center (number 19).
Explorer (number 9) is responsible for the functionality of monitoring the status of a transaction in the network, carried out by standard protocols of the distribution network (number 17), and acts as a processor of RSDC turnover.
Institutional operations (number 10) are carried out on the basis of the principles of asset tokenization (number 25) followed by the issuing and processing functionality of the RSDC network (numbers 24 and 23) using the asset exchange protocol (number 18) and the accounting center for the receipt of collateral in the form of an asset transfer management within the framework of the legislation of the jurisdiction and accounting for FIAT at the clearing partner's site (number 19).
Connection is based on the standard distribution network protocol (number 11)
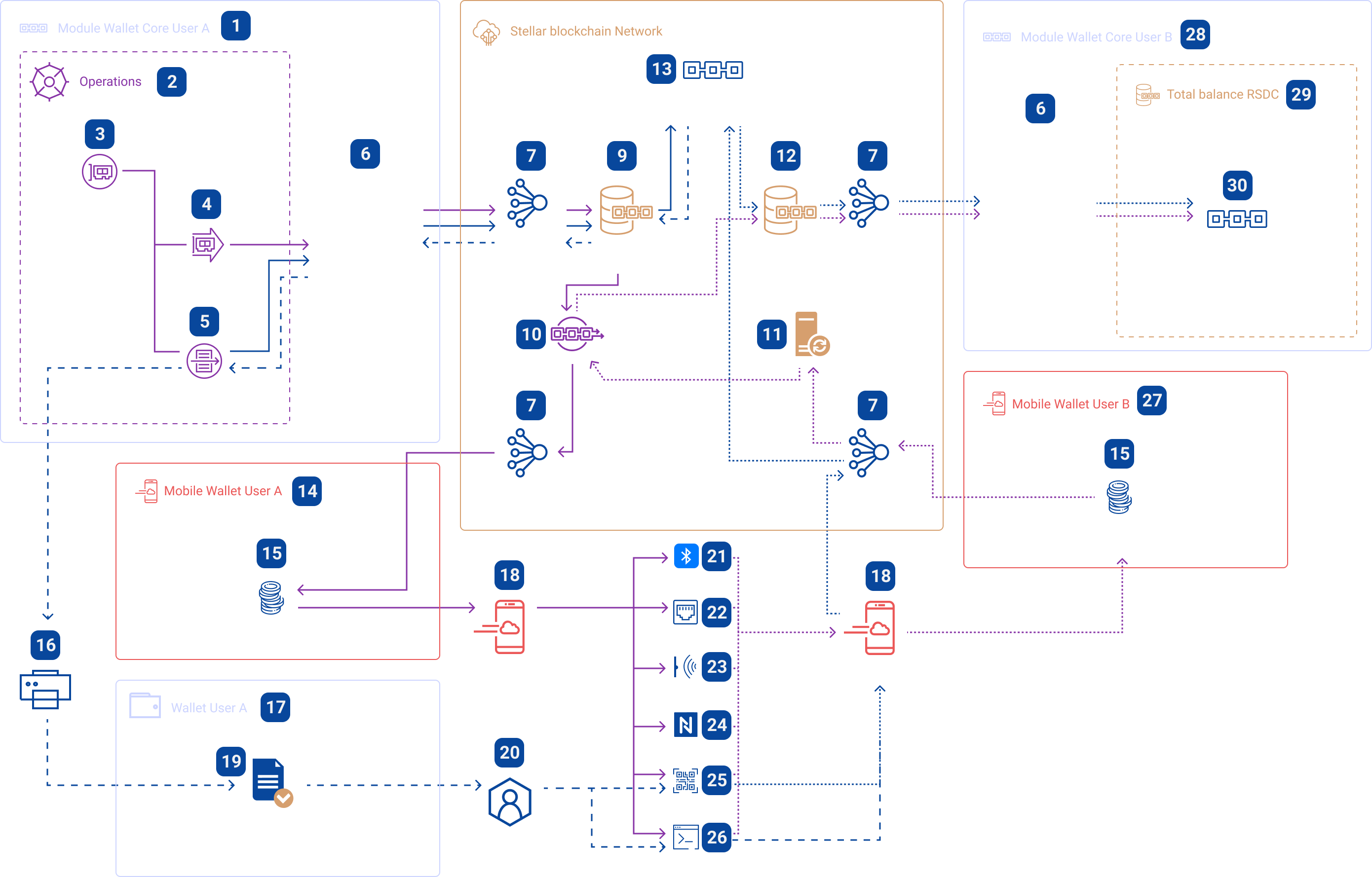
Offline operations with RSDC (number 3) are of two types:
High-level process payments and transfers offline
Process payments and transfers offline
Offline Payments and Transfers Process
This process allows RSDC network users to interact between devices that store token limits using any standard device communication capability (Bluetooth, IR, cable or printed receipt).
Work with RSDC paper form (number 5), issued through application options (number 1) to support operations (number 2).
Work with the volumes stored on the devices interfaced with RSDC (number 4) using the application options (number 1) to support operations (number 2).
ATTENTION: The paper form of RSDC must be accepted by devices online since fraudulent transactions would otherwise be possible in off-line mode.
Through the Wallet Core application (number 1), the RSDC volume limits (number 5) are ordered to generate checks of various RSDC denominations.
The RSDC paper form creation process works as follows:
Through the standard Stellar network connection protocol (number 7), the Wallet Core application (number 6) generates the required number of accounts in the Stellar network (number 13) and transfers from the main account (number 9) of user A the required (defined by the user A) RSDC limits.
Accounts for processing volumes of paper form RSDC (number 13) are closed, i.e. it is impossible to perform any RSDC operations with them, except for the operation of inheritance.
Step 1
Step 2
Inheritance operations are the operation of inheriting the stored volume by another account with the subsequent disposal of the account that was inherited.
The system generates a template for printing the RSDC paper form (number 16).
Step 3
The RSDC paper form must contain the following data: QR-code for scanning by devices with such functionality; document number (public account key in the distribution system) and activation code (private key).
The printed documents representing RSDC paper form (number 19) can be stored by the user in any convenient place, such as a wallet (number 17).
Step 4
ATTENTION: The safety of the RSDC
paper form is the responsibility of the user (number 20), similar to cash.
paper form is the responsibility of the user (number 20), similar to cash.
Processing of the RSDC paper form is only possible using the following communication channels built into the devices (number 18):
QR-code (number 25) - the device must have a QR-code reading interface;
Input line (number 26) - the device must have an interface for entering the account number (public key) and code (private key).
Devices (number 18) can be any of the following: cash registers, ATMs, smartphones, ATMs or other devices with interfaces (number 25 and 26).
Step 5
The receiving device processes the received information displayed on paper (number 19) and implements the protocol of the inherent account number 13 in favor of user account B (number 12).
State of balances information is updated for the user A who issued the paper form (number 1) and for user B - the recipient of funds (numbers 28, 29 and 30).
Step 6
Step 7
After the operations from step 1 to 6 - the paper form RSDC (number 19) can be disposed of, because it becomes non-functional and redundant.
To create a local RSDC storage form (number 4), you need to create a request for the allocation of the required RSDC limit to a special account (number 10) for which RSDC asset transfer operations within the Stellar network (number 8) are provided.
After creating an account for storing funds of offline operations (number 10), the device (number 18) uploads the volumes for local RSDC storage (number 15). Funds are available for offline transactions.
Step 1
Step 2
If it is necessary to carry out offline operations, two devices (user A number 18 and B number 18) must be interconnected by the following types of communications:
Step 3
Bluetooth (number 21)
Cable connection (number 22) such as USB
Step 4
After the exchange of transactions, they are written to local storage (tape - number 15) of the devices of users A and B. Tapes (number 15) are inherently local block chains and follow the principles of block inheritance
When devices are connected to the network, synchronization occurs and the corresponding Stellar network protocol (number 11) is launched, which conducts transactions in the Stellar network (number 8) and transfers funds from the payers' account (number 10) to the beneficiary's account (number 12), with simultaneous updating of the balance sheets of the payer (number 4 and 15) and the beneficiary (number 30).
Step 5
Infrared port (number 23)
NFC (number 24)
By scanning the QR code (number 25)
Simply by entering the transfer activation code (number 26)
ATTENTION: If the integrity of the tape (number 15) is violated,
the device is blocked and investigation procedures are started to detect fraud.
the device is blocked and investigation procedures are started to detect fraud.
Formation and Processing Operations of RSDC Paper Form
Formation and processing of RSDC locally stored on a device
Contact us
To get more information please fill out the form and we will contact you
© 2024 roldmoney.com. All rights reserved by Rold Institution Innovation Research
